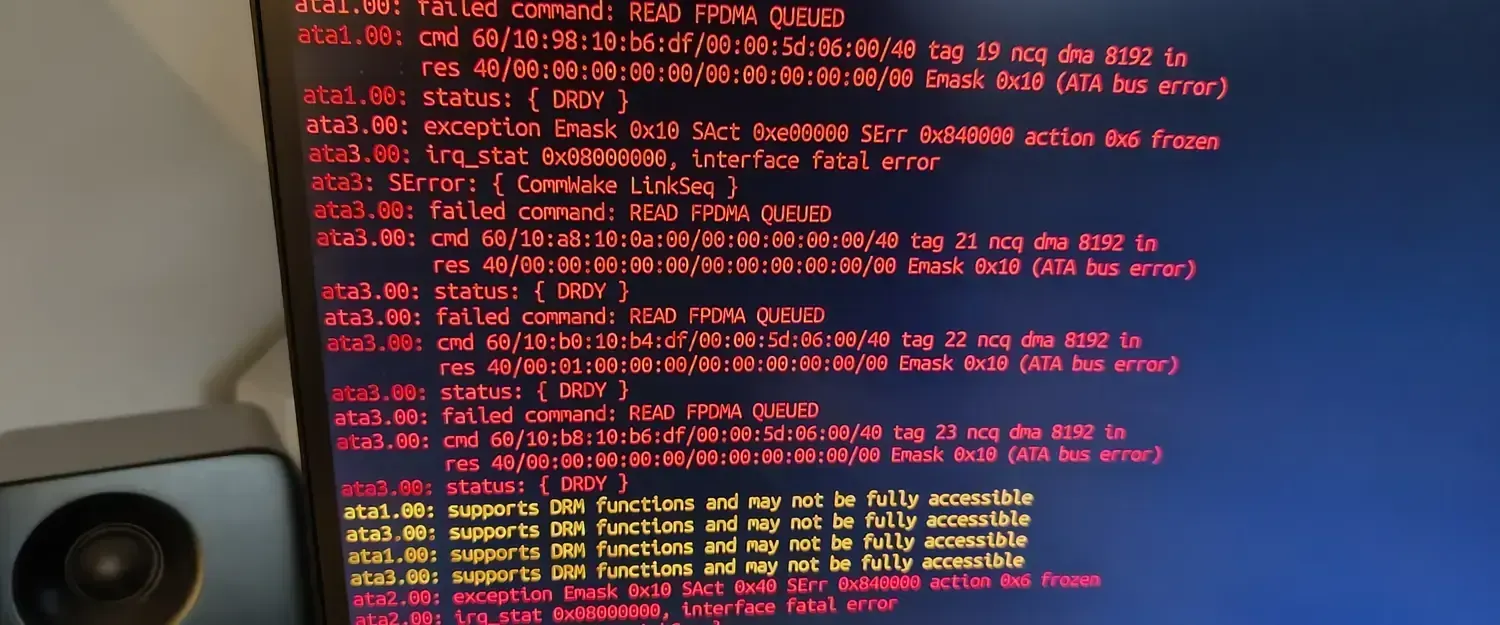
ata1.00: failed command: READ FPDMA QUEUED
Learn how to resolve the “ata1.00: failed command: READ FPDMA QUEUED” error on Ubuntu by adjusting SATA power management settings.

Learn how to resolve the “ata1.00: failed command: READ FPDMA QUEUED” error on Ubuntu by adjusting SATA power management settings.
](https://gagor.pro/2025/01/efficient-dockerfile-templating-for-complex-build-scenarios/images/cover.webp)
Why even consider templating Dockerfiles? Dockerfiles revolutionized the industry with their simplicity. Each instruction creates a new layer in the image, which is automatically cached. This process integrates well with SCM, where you “commit” the results of one stage and move forward with other changes. The process can be easily parameterized with ARG instructions, similar to ENV but provided during the build. This allows for creating highly flexible builds. For most users, this is more than sufficient. However, there’s a notable exception: Docker base images. ...
](https://gagor.pro/2024/05/fix-cannot-rebase-onto-multiple-branches-error-once-and-for-all/images/cover.webp)
A Guide to using git pull --rebase effectively Using git pull --rebase as your default merge strategy offers several benefits, particularly in maintaining a clean and linear commit history, which can simplify collaboration and code review. However, you may occasionally encounter the error “Cannot rebase onto multiple branches”. This article explains why this happens and provides a solution to make git pull --rebase work seamlessly. Benefits of git pull --rebase Linear History: Rebasing applies your local commits on top of the upstream changes, creating a straight line of commits without unnecessary merge commits. This makes the project history easier to read and understand. ...
](https://gagor.pro/2024/05/remove-password-from-pdf-documents/images/cover.webp)
Learn how to remove passwords from PDF documents using the qpdf tool on Linux, making it easier to read protected files on devices like the Pocketbook Touch HD.
](https://gagor.pro/2024/05/optimizing-hugo-sitemaps-to-prioritize-posts-crawling-over-taxonomies/images/cover.webp)
Learn how to optimize your Hugo site’s sitemap by adjusting priority and change frequency settings to improve SEO and guide search engine crawlers effectively.
](https://gagor.pro/2024/04/rising-costs-of-running-legacy-amazon-rds-systems/images/cover.webp)
Understand the rising costs of maintaining legacy Amazon RDS systems and explore the new RDS Extended Support option for MySQL and PostgreSQL.
](https://gagor.pro/2024/04/create-a-virtual-bookshelf-with-hugo-and-papermod/images/cover.webp)
Learn how to create a virtual bookshelf on your Hugo site using the PaperMod theme, allowing you to organize and share your reading list with ease.

Learn how to install Oracle Instant Client on Ubuntu 24.04 using both recommended and alternative methods, with a focus on Docker images.
](https://gagor.pro/2024/03/automatically-setting-lastmod-in-hugo-pages-with-git-modification-date/images/cover.webp)
Learn how to automatically set the ’lastmod’ parameter in Hugo pages using Git modification dates to improve SEO and expedite search engine indexing.
](https://gagor.pro/2024/03/how-old-are-official-docker-images-2024-edition/images/cover.webp)
Discover the current age and update status of various official Docker images, including CentOS, Ubuntu, and Debian, in the 2024 edition of this analysis.